See the Aeson® Animation Video
WHAT CARMAT IS ABOUT
CARMAT aims to meet a major public health challenge related to cardiovascular diseases, namely heart failure, the leading cause of death in the western world.
More specifically, CARMAT aims to provide a lasting solution for the treatment of terminal heart failure, a disease for which there are very few effective options today, the main one being heart transplants.
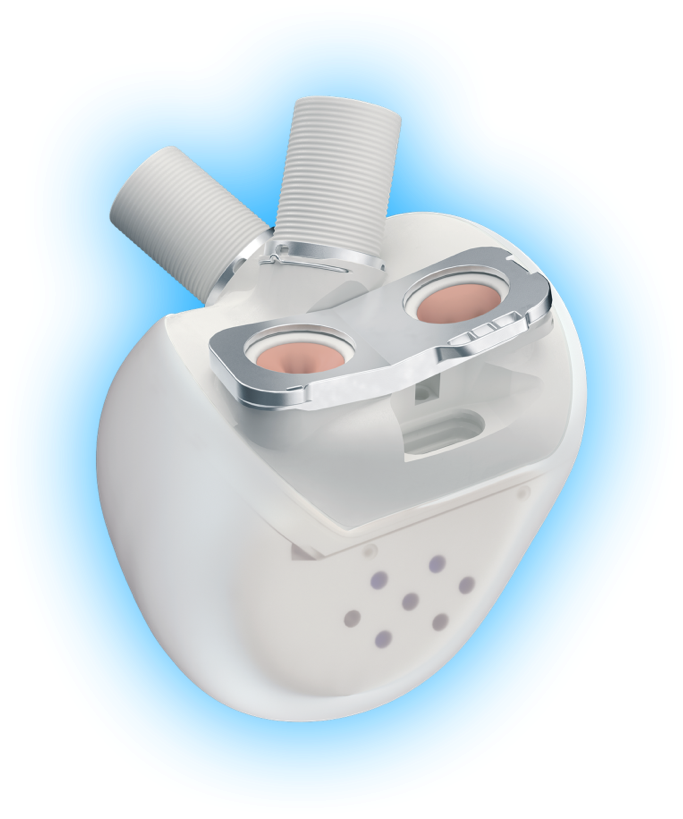
AESON®
- Aeson® is a Total Artificial Heart. Unlike other mechanical circulatory support devices, such as LVAD (left ventricular assist devices) that assist the left ventricle of the heart, Aeson® Total Artificial Heart replaces booth ventricles of the heart.
- Aeson® System is a single-use device consisting of an implanted prosthesis and a set of equipment and materials that together provide a Physiologic Heart Replacement Therapy1.
In the future, the company's ambition is to make Aeson® the first alternative to a heart transplant, and thus provide a therapeutic solution to people suffering from end-stage biventricular heart failure, who are facing a well-known shortfall in available human grafts.
- Aeson® is commercially available as a bridge to transplant (BTT) in the European Union and other countries that recognize CE marking.
- Aeson® is also currently being assessed within the framework of an Early Feasibility Study (EFS) in the United States.
Aeson® System overview

The implantable component, Aeson® Prosthesis with percutaneous driveline, mimics a natural heart function and is powered, configured and monitored by the External System and the Tablet.
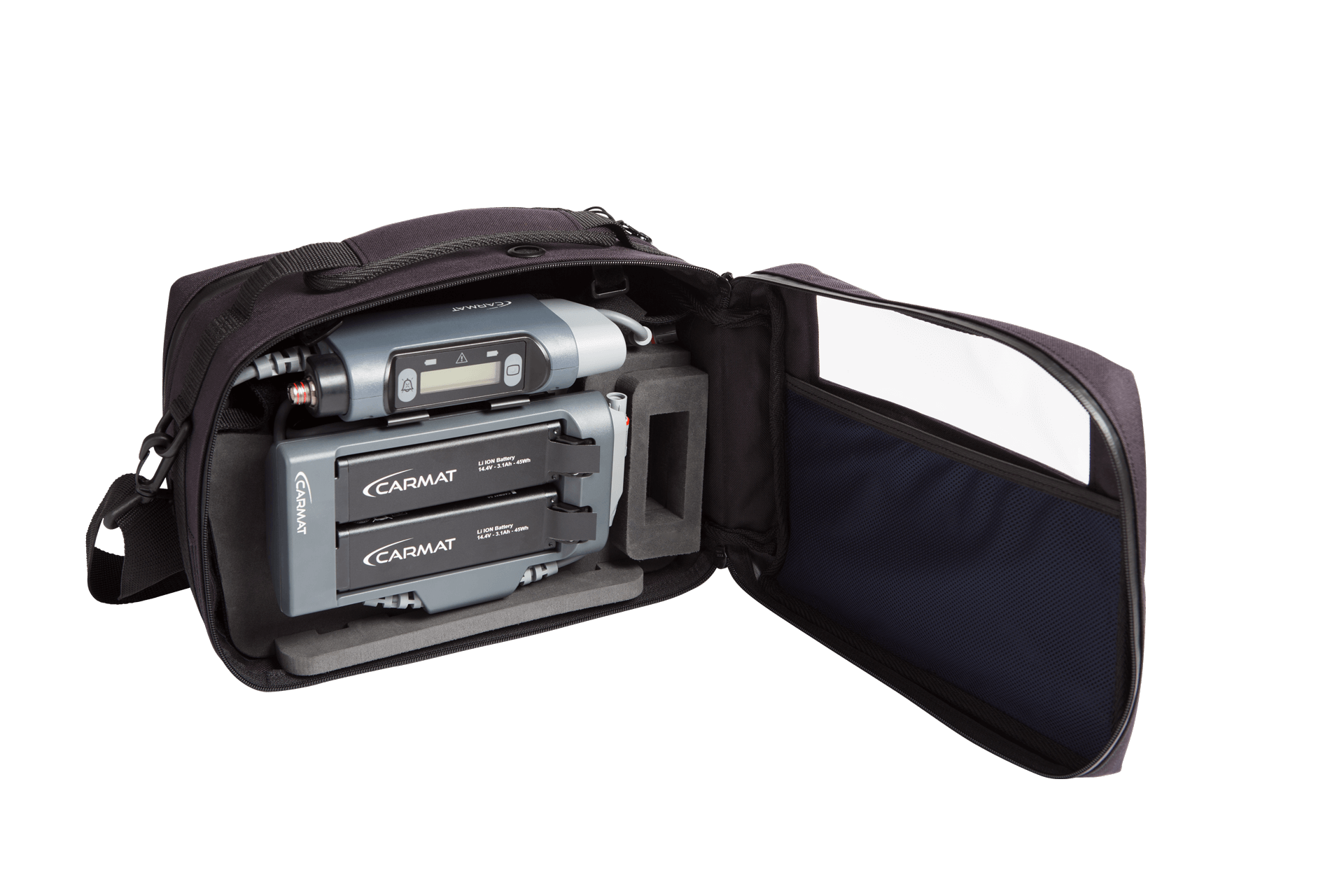

The External System provides the
patient with the mobility needed to
lead a near-normal life.
The External
System is defined as the external
equipment contained in Aeson® Carry
Bag and consists of a Controller, a
Battery Pocket with four Batteries and a
Patient Cable.
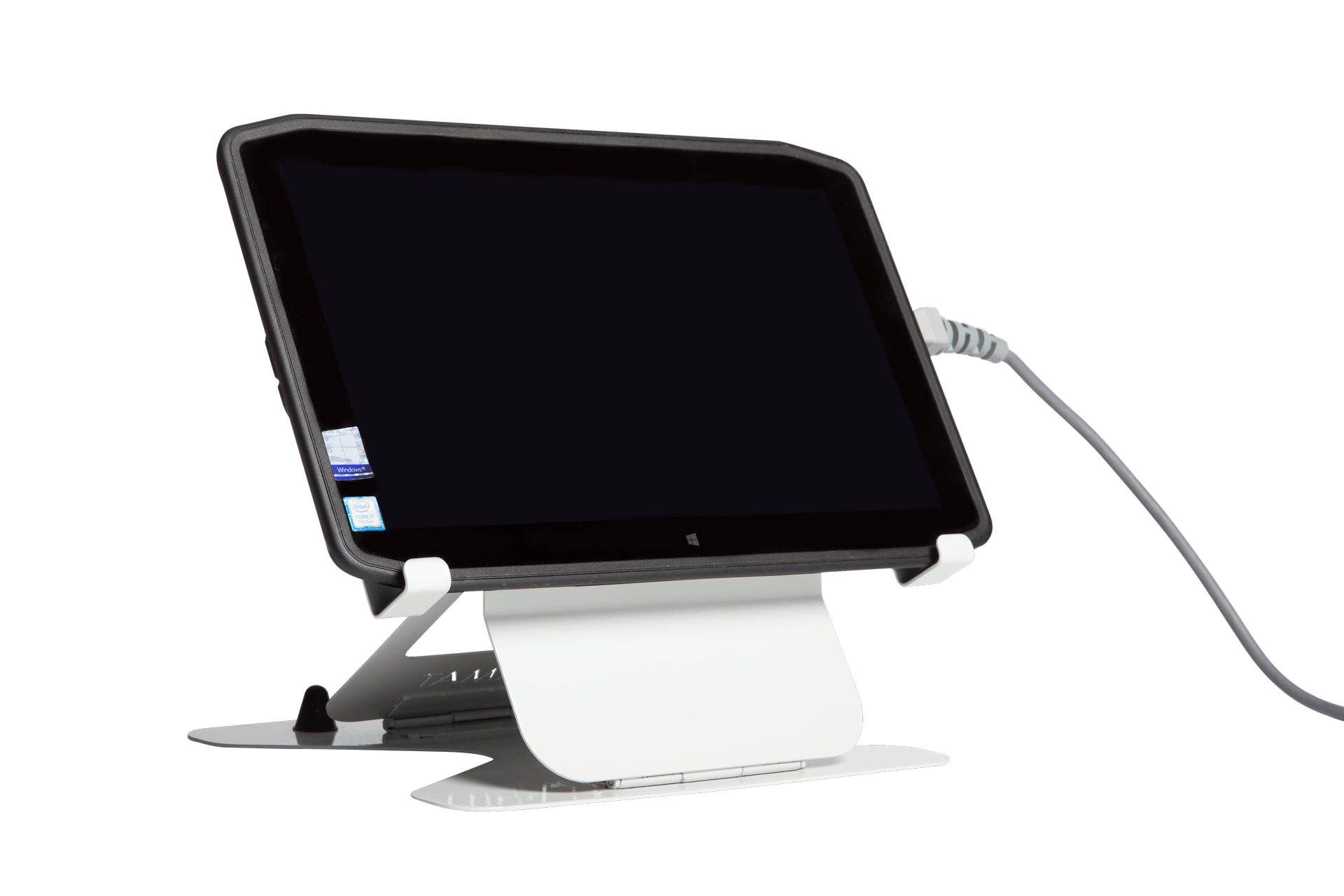
The Tablet is used by clinicians to operate the Aeson®
Prosthesis during implantation.
It is also used for
Patient follow-up in post-operative care.

- Savarese G, Lund LH. Global Public Health Burden of Heart Failure. Cardiac Failure Review. 2017;03(01):7–11.
- Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56-e528.
- Ammar KA, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of heart failure stages: application of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure staging criteria in the community. Circulation. 2007;115(12):1563-70.
- Stehlik J. et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: 29th Official Adult Heart Transplant Report—2012 J Heart Lung Transplant October 2012 Volume 31, Issue 10, Pages 1052–1064
- Miller L. W. Is Left Ventricular Assist Device Therapy Underutilized in the Treatment of Heart Failure? Circulation 2011;123;1552-1558
- K.K.Khush et al., The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-eight Adult Heart Transplantation Report—2021; Focus on recipient characteristics.
- The New York Heart Association (NYHA)
Image Source:
nitpicker/Shutterstock.com
Travel_with_me/Shutterstock.com
iStock.com/lucamato

















